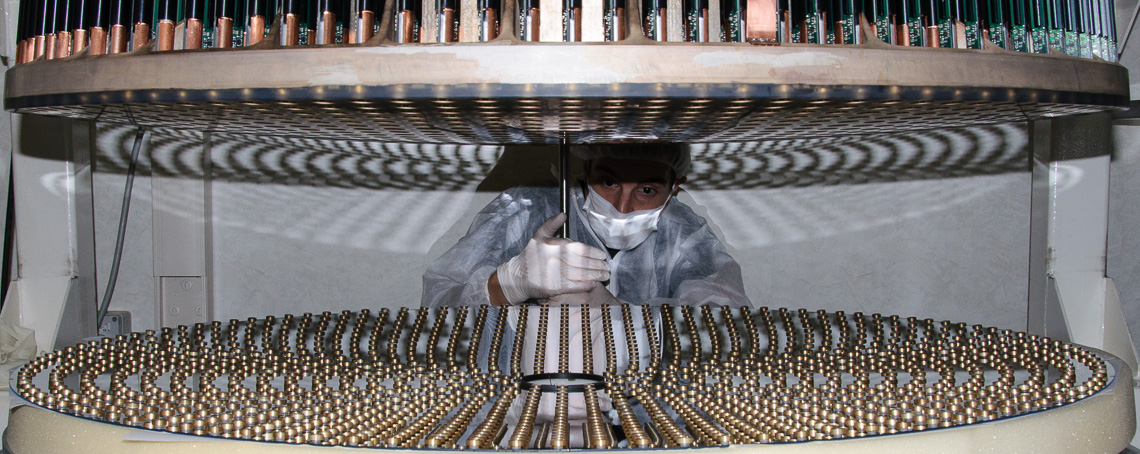
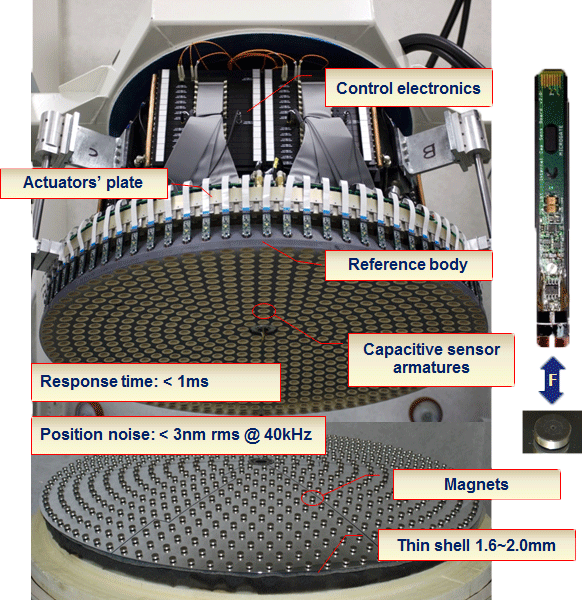
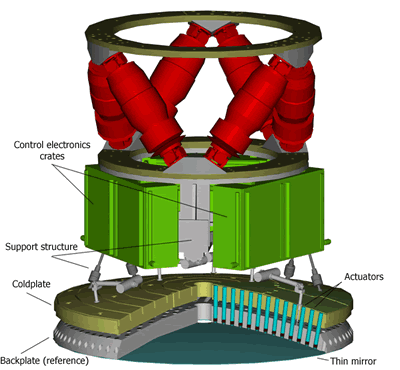
In its current implementation, the "contactless" adaptive mirror is based on a continuous, thin mirror (~1.6mm) actively controlled in position and shape by a large number of force actuators (voice coil motors). During operation, the thin mirror "levitates" controlled by the electromagnetic field generated by the actuators. There is no mechanical contact between actuators and thin mirror. Each actuator is made by a fixed coil wound on a cold finger and a moving magnet, glued to the rear surface of the thin adaptive mirror. The actuators are fixed to a cold plate that provides cooling and mechanical support. A stiff (~50 mm thick), thermally stable structure (backplate) provides the position reference for the thin mirror.
The gap between backplate and thin mirror is measured by capacitive sensors, co-located with the actuators. Typical operating gap between backplate and deformable mirror is between 40 and 120µm. The adaptive mirror control system is based on custom-designed high speed digital and analog electronics. About 70,000 times every second, the gap of the mirror at each actuator position is read, compared with the desired gap, and a proper actuator force is computed and commanded.
The mirror position and shape is updated at a typical rate of 1 millisecond.
The adaptive mirror concept has several advantages over other conventional adaptive optics layouts for telescopes:
For more detailed info, please read this paper ("Contactless thin adaptive mirror technology: past, present and future") presented at SPIE 2010 in San Diego.
And for a visual demonstration watch this short video taken from a German documentary broadcasted by n-tv.






